SEATTLE, June 19, 2023 /PRNewswire/ — Marler Clark, Inc., PS, The Food Safety Law Firm, is publishing a consumer information guide to navigate the current multi-state Cyclospora outbreak that has yet to be linked to a specific food product.
“Cyclospora illnesses have been a growing concern in the United States and around the world linked to fresh fruits and vegetables,” says Bill Marler.
The current Cyclospora Outbreak
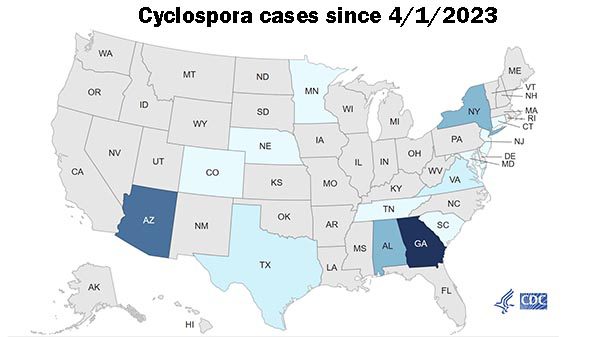
According to the CDC, as of June 6, 2023, a total of 97 laboratory-confirmed cases of cyclosporiasis have been reported from Arizona, Colorado, Nebraska, Texas, Minnesota, Alabama, Tennessee, Georgia, South Carolina, Virginia, Maryland, New Jersey, New York, Connecticut, and New York City. Sick people range in age from 16 to 92 years, with a median age of 48, and 71% are female. The median illness onset date is April 27, 2023 (range: April 1 to May 25). Of 96 people with information available, 16 have been hospitalized. No deaths have been reported. The Colorado Department of Public Health and Environment is currently investigating an outbreak of Cyclospora at Ridgway Tacos del GNAR. As of June 15, there have been 62 cases reported in Colorado since May 1, 2023.
What is Cyclospora?
Cyclospora is a parasite composed of one cell, too small to be seen without a microscope. Cyclospora cayetanensis is the only species of this organism found in humans.
Cyclosporiasis is an intestinal illness caused by the parasite Cyclospora cayetanensis, which is transmissible by ingestion of fecally contaminated food or water. Cyclosporiasis is most common in tropical and subtropical regions of the world. In the United States, foodborne outbreaks of cyclosporiasis have been linked to various types of imported fresh produce (e.g., basil, raspberries, and snow peas). Outbreaks of cyclosporiasis in humans have been reported mostly from North America, from the infection sources of contaminated fresh food products, such as soft fruits (raspberries), leafy vegetables (coriander, basil, and mixed salad), and herbs. Soil is another possible infection source, particularly in areas with poor environmental sanitation.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) has been conducting national surveillance for cyclosporiasis since it became a nationally notifiable disease in January 1999. As of 2015, cyclosporiasis was a reportable condition in 42 states, the District of Columbia, and New York City (NYC).
While cyclosporiasis cases are reported year-round in the United States, cyclosporiasis acquired in the United States (i.e., “domestically acquired,” or cases of cyclosporiasis that are not associated with travel to a country that is considered endemic for Cyclospora) is most common during the spring and summer months. The exact timing and duration of U.S. cyclosporiasis seasons can vary, but reports tend to increase starting in May. In 2020, multiple outbreaks of cyclosporiasis were identified and found to be linked to different produce items. As of September 23, 2020, the CDC documented 1,241 laboratory-confirmed cases of cyclosporiasis in people who had no history of international travel during the 14-day period before illness onset.
What are the typical symptoms of Cyclospora infection?
Cyclospora infects the small intestine (bowel) and usually causes watery diarrhea, bloating, increased gas, stomach cramps, and loss of appetite, nausea, low-grade fever, and fatigue. In some cases, vomiting, explosive diarrhea, muscle aches, and substantial weight loss can occur. Some people who are infected with Cyclospora do not have any symptoms. The time between becoming infected and becoming ill is usually about one week. If not treated, the illness may last from a few days up to six weeks. Symptoms also may recur one or more times (relapse). In addition, people who have previously been infected with Cyclospora can become infected again.
Where does Cyclospora come from?
The modes of transmission of C. cayetanensis are still not completely documented, although fecal–oral transmission is the major route. Direct person-to-person transmission is unlikely. Indirect transmission can occur if an infected person contaminates the environment, the oocysts sporulate under the right conditions, and then contaminated food and water are ingested. The role of soil in transmission has also been proposed.
The dissemination of infective Cyclospora oocysts via water, soil, and unprocessed foods (e.g., fruits and vegetables, including ready-to-eat salads) is enabled by their small size (8–10 µm), low specific gravity, and high infectivity. Such oocysts can survive for weeks to months in water and food, depending on the environmental temperature, and are resistant to the routine sanitization or chemical disinfection procedures used in irrigation systems, recreational waters, or drinking water treatment plants.
How is Cyclospora diagnosed?
Cyclosporiasis is usually diagnosed symptomatically in clinical settings, including the presence of watery diarrhea, abdominal cramping, and bloating. In untreated, immunocompetent people, the diarrhea can last from days to weeks to a month or more, and can wax and wane, with variable oocyst shedding. Oocysts can continue to be shed (intermittently or continuously) by non-symptomatic people, and symptoms can also persist in the absence of oocysts in feces.
What are the serious and long-term risks of Cyclospora infection?
Cyclospora has been associated with a variety of chronic complications such as malabsorption, reactive arthritis, and cholecystitis (inflammation of the gallbladder). Since Cyclospora infections tend to respond to the appropriate treatment, complications are more likely to occur in individuals who are not treated or not treated promptly. Extraintestinal infection also appears to occur more commonly in individuals with a compromised immune system.
Although human cyclosporiasis is usually not fatal in developed countries such as the United States, protracted diarrhea often leads to dehydration, particularly in infants who are at greatest risk of severe dehydration and death, especially if cyclosporiasis is complicated by infections with other pathogens (viral, bacterial, or parasitic—e.g., Cryptosporidium and Giardia), malnutrition, or malabsorption, particularly in underprivileged communities.
According to the CDC, the recommended treatment is a combination of two antibiotics, trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, also known as Bactrim, Septra, or Cotrim. It is advisable for people who have diarrhea to also rest and drink plenty of fluids.
About Marler Clark, The Food Safety Safety Law Firm
Marler Clark, is the nation’s leading law firm representing victims of Cyclospora outbreaks. The Cyclospora Attorneys at Marler Clark have represented victims of foodborne illness for over 30 years, recovering over $850 million for their clients. Marler Clark is the only law firm in the nation with a practice focused exclusively on foodborne illness litigation. If you or a family member became ill with a Cyclospora infection after consuming food and you are interested in pursuing a legal claim, contact Marler Clark for a free case evaluation.